Periodontal Disease
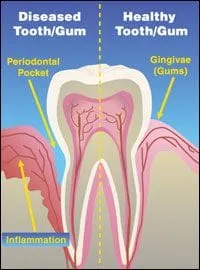
Indications of periodontal disease include: swollen, painful, or bleeding gums, bad breath, and loose or sensitive teeth. Unfortunately, periodontal disease is not always obvious. Bacterial infection may be silently and progressively destroying the soft tissues and bone that support the teeth.
There are many factors that contribute to periodontal disease, such as oral hygiene habits (grinding or clenching), poorly fitting dentures or bridges, stress, general health, medications, systemic diseases, genetics, poor diet, and tobacco use, which can also influence treatment effectiveness and disease recurrence.
Stages of Periodontal Disease
Gingivitis
is a mild form of the disease, caused by bacteria irritating the gums. Plaque, a sticky film that forms on the teeth and gums hardens into calculus, which forms a rough surface along the gum line on which more plaque accumulates, causing more irritation and swelling. Although this usually results in sore, bleeding gums, bad breath and spaces between the gums and teeth (pockets) there is no damage to the bone at this point.
Periodontitis
occurs when plaque and possibly calculus are found below the gum line. The gums are irritated and bright red. They bleed easily and shrink back, or recede. The ligaments that attach the tooth roots to the bone break down and the gum detaches and pulls away from the teeth. The pockets deepen and fill with more bacteria. The damage to ligaments and bone results in loose teeth.
Advanced periodontitis
is the most severe stage of the disease process. When periodontitis progresses to the advanced stage, pockets deepen and may fill with pus. There is typically swelling around tooth roots and sensitivity to hot or cold. As bone loss increases, tooth loss generally occurs. Sometimes the teeth need to be removed to preserve the overall health of your mouth.




